Brief description
The European Plate Observing System (EPOS) is a pan-European infrastructure for solid Earth science, providing virtual access to data, products and services as well as physical access to facilities for a broad community of users.
EPOS integrates the existing (and future) advanced European facilities and infrastructures into a single, distributed, sustainable infrastructure taking full advantage of new e-science opportunities.

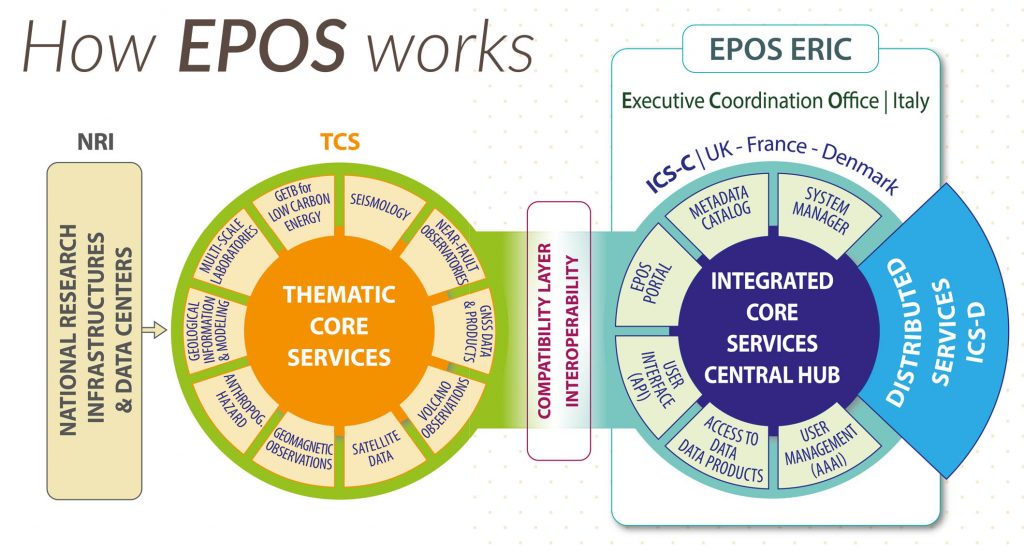
EPOS consists of four elements that form the scientific/technical backbone of the whole enterprise:
- National Research Infrastructures (NRI) – provide access to data and services for diverse communities at a national level. European NRIs include geophysical networks, laboratories, and modelling facilities for solid Earth studies.
- EPOS ERIC – is the European Consortium that coordinates the EPOS Research Infrastructure. The ERIC legal framework aims to provide an effective governance plan to the TCS and the ICS.
- Thematic Core Services (TCS) – are transnational entities that represent different domains of the solid Earth (seismology, volcanology, geodesy, geology). Moreover, the TCS will provide access to new data products and services to the user community
- Integrated Core Services (ICS) – is the new digital infrastructure giving access to multidisciplinar data, products (including synthetic data from simulations, processing and visualization tools) and services, available in the TCS and NRIs various users, including but not limited to the scientific community, economic environment and general public.
EPOS Vision
- To ensure sustainable and universal use and re-use of multidisciplinary solid Earth science data and products fostering state-of-the-art research and innovation.
- To make possible a better understanding of the Earth surface and sub-surface dynamics and use this progress in science for the assessment of geo-hazards and sustainable use and exploitation of geo-resources.
The EPOS-RO context
Romania, represented by the National Institute for Earth Physics (INCDFP), has been involved in the EPOS project from the beginning and participated in all phases of the project (Preparation Phase, Implementation Phase and Sustainability Phase) along with other Universities and European research institutions.
Romania’s involvement in EPOS is in line with the national strategic objectives to consolidate, integrate and assure an adequate use of its research infrastructures responding to the requirements of major science and technology research initiatives and programs.
During the 8th EPOS ERIC General Assembly, organised in December 2020, Romania joined the EPOS ERIC as an official member.
Founded in 2018, EPOS ERIC is currently joined by 14 countries: thirteen countries as official members (Belgium, Denmark, France, Greece, Iceland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, and the United Kingdom), and one country, Switzerland, participating as an observer. Find out here what is EPOS-RO.
The advantages of Romania’s participation to EPOS
- initiating innovative research based on the access of EPOS services;
- access to Thematic Services -TCS (Seismology, GNSS, Induced Seismicity, etc.) including access to experimental facilities;
- access to Integrated Services (ICS) for visualization and processing of standardised and quality validated data;
- developing new research products and services based on observation data through the exchange of best practices;
- increasing the use and exploitation of recorded and stored observation data by national research infrastructures through national and international research and cooperation;
- establishing connections with other networks and infrastructures in the field of Earth Sciences (marine, space and environmental sciences etc.).
